Next-Gen Software: Build Fast with Vibe Coding
Silke Kanes, Member of the Board of the eco Association, explains how vibe coding is changing software development. She explains the new phenomenon – AI-powered development that breaks barriers, accelerates prototyping, and empowers tech and business teams to build smarter, faster, and more creatively than ever before. But: This breakthrough is no cure-all for every challenge.

© mesh cube | istockphoto.com
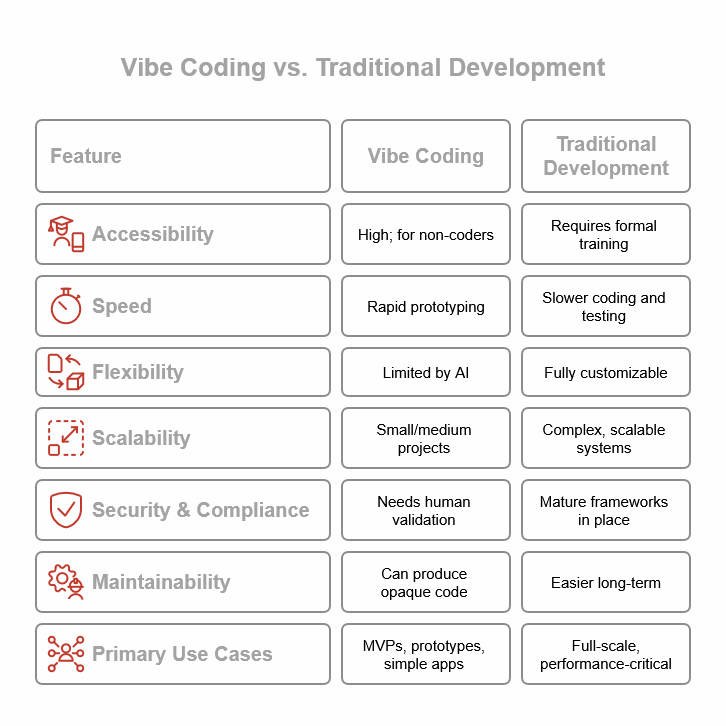
Vibe coding is an innovative approach that leverages artificial intelligence (AI) and automation to make software development faster, more intuitive, and accessible. By combining natural language input with smart AI-powered tools, it enables the creation of tailored software solutions even without deep programming expertise. However, technical skill requirements vary widely depending on the specific platform – making it important to choose the right tool according to your experience and project needs. And it comes with some limitations and challenges!
What is vibe coding?
Introduced in early 2025 by AI pioneer Andrej Karpathy, vibe coding fundamentally changes how software is built. Instead of manually writing lines of code, users describe what they want in everyday language, and AI models translate these prompts into functional, editable code. Unlike traditional low-code or no-code platforms that can obscure or limit control over software internals, vibe coding keeps code transparent and customizable, positioning AI as a collaborative partner rather than a mere assistant.
This shift allows developers to focus on high-level goals and design intentions while AI automates repetitive and boilerplate programming tasks. The process embraces a “code first, refine later” mindset, perfectly aligned with agile principles of fast prototyping, iterative development, and cyclical feedback. It encourages experimentation and creativity, promoting a new dialog between human intuition and machine-generated implementation.
Current tools and platforms
The vibe coding ecosystem has rapidly diversified to serve a broad spectrum of users:
- GitHub Copilot and Cursor focus primarily on seasoned developers. These tools provide context-aware suggestions, real-time code generation, and seamless integration into complex development environments like Visual Studio Code. While powerful, they require working knowledge of programming languages and frameworks to fully realize their benefits.
- Diamond by Graphite enhances development workflows by integrating AI-powered code reviews and automated quality assurance. Such tools are indispensable for maintaining high code quality in professional software projects, though they demand an advanced understanding of software engineering practices.
- On the other end of the spectrum, platforms like Lovable, Wegic, and Replit – especially in their beginner modes – are designed for users with little or no coding background. These platforms translate natural language descriptions into prototypes with no-code or low-code interfaces, managing syntax, deployment, and scaling behind the scenes. This lowers barriers, empowering designers, product managers, marketers, and citizen developers to create usable apps and interactive experiences.
This layered tooling approach ensures vibe coding is inclusive, supporting novices and experts alike.
Use cases in concepting and prototyping
Vibe coding excels at transforming ideas into minimal viable products (MVPs) at an unprecedented pace. Early phase projects benefit from rapid iteration cycles where users describe interface designs, user interactions, and logic flows in simple terms. The AI generates code for front-end layouts, back-end services, and workflows, which can be tested immediately.
This approach enables product teams to validate concepts quickly with real users, adjust features via conversational prompts, and iterate without extensive hand-coding. It supports an agile, lean development process while democratizing software creation to include non-technical stakeholders.
Limitations and challenges
While promising, vibe coding isn’t a silver bullet:
Complexity and scalability: Large-scale applications requiring intricate architectures, load balancing, and optimized performance still need expert development teams.
Security and compliance: Regulatory requirements for data protection and auditability demand in-depth human oversight that AI alone cannot guarantee.
Maintainability: AI-generated code sometimes lacks documentation or clear structure, making long-term maintenance and debugging challenging.
Debugging and customization: Complex bugs and nuanced feature requests often require manual coding and deep technical expertise.
Thus, vibe coding currently complements rather than replaces traditional development methods, especially in mission-critical or enterprise-grade software.
A reflection on learning programming: My personal perspectiveSome weeks ago, I was asked if I would recommend that young people learn programming and study computer science given advances like vibe coding. My answer was a resounding “yes!” but with nuances. While vibe coding lowers barriers and expands the pool of who can create software, understanding core programming and computer science fundamentals remains invaluable. Programming teaches problem-solving, logical thinking, and the deeper principles behind how software works. These are skills that help to critically evaluate and effectively guide AI-generated solutions. |
Moreover, complex software systems, architecture design, performance optimization, and security concerns still require human expertise. As AI tools augment rather than replace developers, having a solid foundation allows young professionals to better collaborate with AI, adapt to evolving technologies, and build innovative solutions responsibly.
In short, learning programming equips the next generation not just to consume AI-powered tools but to innovate safely and push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Conclusion and call to action
Vibe coding is reshaping software development – making it more inclusive, faster, and creatively collaborative. Aligning your choice of platform with your team’s technical skills and goals is critical to success.
To truly grasp its power, try vibe coding yourself! Platforms like Lovable, based in Sweden, offer free accounts that let anyone describe an idea in natural language and watch AI turn it into a functioning app. Dive in, explore, and let the “vibes” inspire your next digital project.
📚 Citation:
Kanes, Silke. (November 2025). Next-Gen Software: Build Fast with vibe coding. dotmagazine. https://www.dotmagazine.online/issues/ai-automation/vibe-coding-software-development
Silke Kanes is the newly elected Board Member for software as a service at the eco – Association of the Internet Industry. Having spent many years in executive positions at software manufacturers, where she was responsible for product development, she now works as a strategic advisor to entrepreneurs on digital and corporate culture transformations.
FAQ
1. What is vibe coding and how does it differ from traditional development?
Vibe coding uses natural‑language prompts and AI tools to generate working software quickly, unlike traditional development which involves writing each line of code by hand. Kanes explains it lowers barriers while keeping human oversight of design and architecture.
2. Who can benefit from vibe coding and what are the typical use‑cases?
According to Kanes, vibe coding is useful for:
• Rapid prototyping and MVPs
• Empowering non‑programmers (designers, product managers)
• Accelerating development in agile teams
However, it’s less suitable for large, complex systems without expert support.
3. What are the key limitations and risks of vibe coding?
Kanes highlights several risks including:
• Scalability and architecture complexity
• Security, compliance and auditability concerns
• Maintainability of AI‑generated code lacking documentation or structure
Thus vibe coding complements rather than replaces traditional software engineering.
4. Should everyone stop learning programming because of vibe coding?
No. Kanes argues that programming fundamentals remain crucial: they enable critical thinking, deep understanding of system behaviour, and meaningful collaboration with AI tools — so yes, young professionals should still learn core computer science.
5. How can organisations choose the right vibe coding tool?
Kanes suggests considering factors such as:
• Team’s technical expertise
• Project size and criticality
• Tool’s transparency and customization options
• Security, governance and integration capabilities
Choosing the right tool is crucial for success.
6. What practical steps should companies take to adopt vibe coding responsibly?
Based on the article, companies should:
• Start with pilot projects
• Ensure human review and code audit processes
• Provide training for staff
• Align tools with compliance, architecture and maintenance strategies




